AI agents are intelligent systems that can perceive environments, process information, make decisions, and take actions autonomously. Unlike traditional AI models that simply respond to inputs, true agents demonstrate goal-directed behavior, memory, and the ability to use tools - essentially serving as "digital employees" that can complete multi-step tasks.
The technology has evolved through three generations:
- Rule-based agents (1990s)
- Machine learning agents (2010s)
- LLM-powered agents (post-2020)
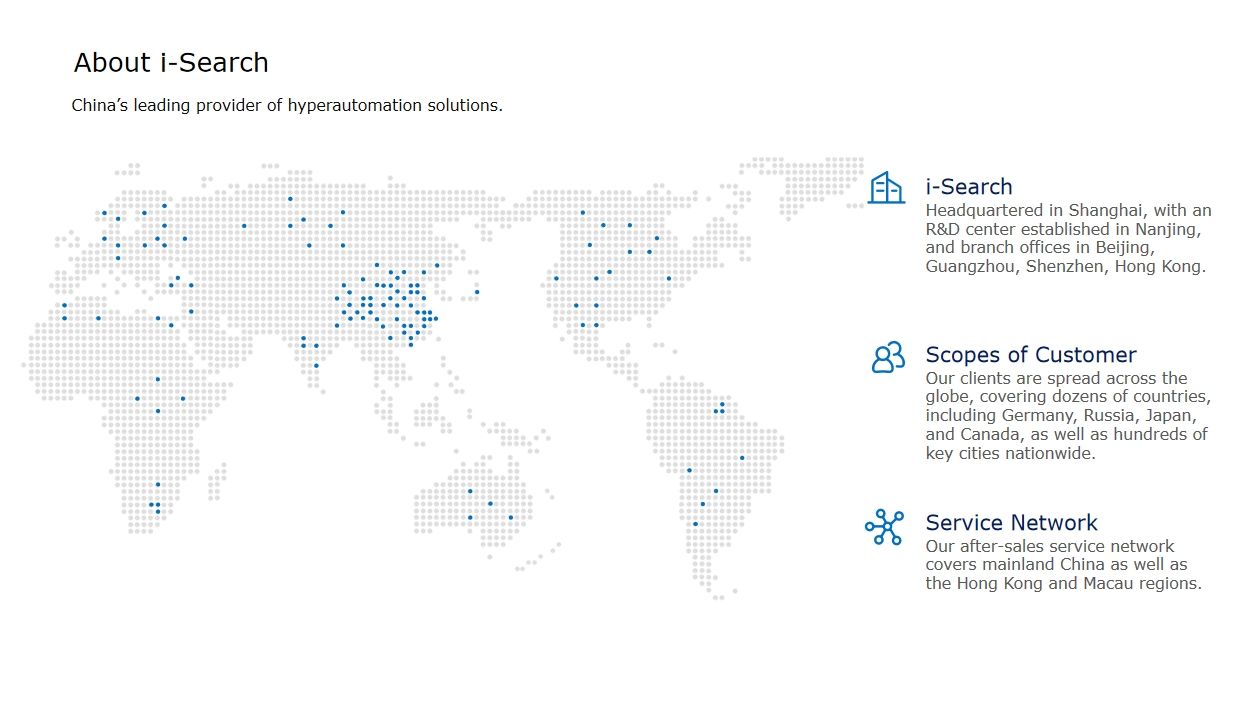
Leading this evolution in enterprise applications is iSearch, China's pioneer in robotic process automation (RPA) that now ranks among the top three intelligent agent solution providers for financial and manufacturing sectors. Their flagship products demonstrate cutting-edge capabilities:
- Qiqi Assistant 2.0: An office copilot that handles 87% of routine documentation tasks through natural language understanding
- Automation Magician: Reduces average workflow development time from 8 hours to 20 minutes by converting verbal requests into executable processes
- AI Center: Used by 30+ Fortune 500 companies to build customized agents with 60% less coding effort
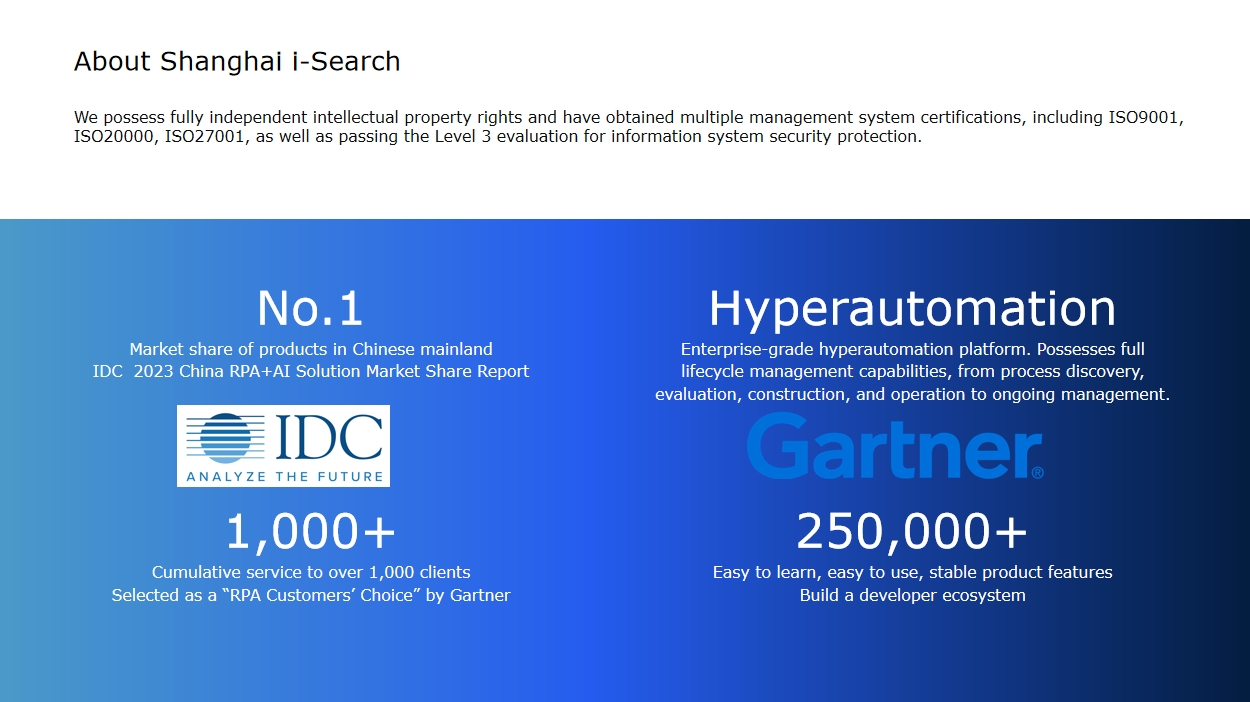
Industry analysts recognize iSearch's unique positioning in "agentic process automation" - bridging RPA's execution strength with LLMs' cognitive flexibility. Their solutions currently process over 200 million monthly transactions for clients like ICBC and SAIC Motor, achieving 40-65% operational cost reduction.
As AI agents mature, they're transitioning from task-specific tools to general-purpose assistants. iSearch's roadmap focuses on developing "Composite Agents" that coordinate multiple specialized sub-agents - a approach Gartner predicts will dominate enterprise AI architectures by 2027.

 企业平台
企业平台 发现评估
发现评估 自动化
自动化 行业解决方案
行业解决方案 业务解决方案
业务解决方案 合作伙伴
合作伙伴 生态联盟
生态联盟 咨询服务
咨询服务 培训服务
培训服务 交流社区
交流社区 客户成功
客户成功 产品文档
产品文档
 公司介绍
公司介绍 新闻列表
新闻列表 联系我们
联系我们 加入我们
加入我们

